PUBLIC FINANCE
Governments are still spending billions subsidizing oil, gas and coal. We need to #StopFundingFossils and start investing in the future.
OVERVIEW OF WORK
Since the Paris Agreement, G20 governments have continued to finance more than USD 77 billion dollars annually in fossil fuels through multilateral development banks (MDBs), bilateral development finance institutions (DFIs), and export credit agencies (ECAs). This is three times the support they provide to clean energy. Beyond providing this direct monetary backing, these institutions reduce perceived risk and provide a government stamp of approval on fossil fuel projects that often serves to crowd in private finance. While recently the level of fossil fuel support has started to drop, institutional policies to exclude fossil fuel finance are needed to ensure this progress continues.
While a number of public finance institutions committed to ending coal finance in the early 2010s, it wasn’t until 2017, following years of campaign pressure by Oil Change and others, that the World Bank made a meaningful commitment to stop financing for upstream oil and gas. Following an intense campaign effort, in 2019 the European Investment Bank committed to ending nearly all oil, gas and coal finance. Recently, the UK announced it would end overseas oil and gas finance, and the EU and US, among others, have signalled that they intend to follow suit. Building off these successes, OCI is now working to secure further commitments from governments and public finance institutions on ending public finance for fossil fuels.
LATEST PROGRAM POSTS
Today the outgoing Dutch Minister for Climate and Energy Policy, Rob Jetten, published an analysis of the Netherlands’ fossil fuel subsidies, estimating these at between €39.7 and €46.4 billion a year, more than 4% of the Netherlands’ GDP.
The turnout wildly exceeded expectations, proof that this summer's record heat, mega floods, and severe weather are putting the climate crisis, and the fight against fossil fuels, at the forefront of peoples' minds. The turnout was global.
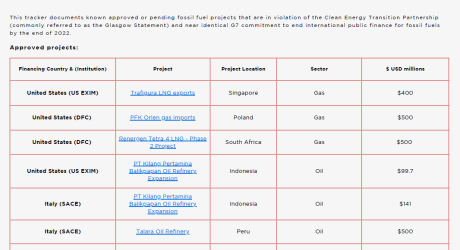
Rich countries have continued to approve USD 4.4 billion in international public finance despite committing to end this support by the end of 2022. Six countries including the United States, Germany, Italy and Japan have at least 26 fossil fuel projects awaiting approvals, with Germany having the biggest number of projects pending.
*Updated February 2024* Oil Change International analysis shows that several major countries continue to pump $6.2 billion in public finance into international fossil fuel projects despite committing to end this support by the end of 2022.
LATEST PROGRAM RESEARCH
Despite the urgent need to phase out fossil fuels, Japan is driving the expansion of liquified gas (LNG) and other fossil-based technologies like ammonia co-firing, worsening the climate crisis and harming communities and ecosystems.
*Updated February 2024* Oil Change International analysis shows that several major countries continue to pump $6.2 billion in public finance into international fossil fuel projects despite committing to end this support by the end of 2022.
New research shows that Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) countries supported fossil fuel exports by an average of USD 41 billion from 2018-2020, almost five times more than clean energy exports ($8.5 billion).